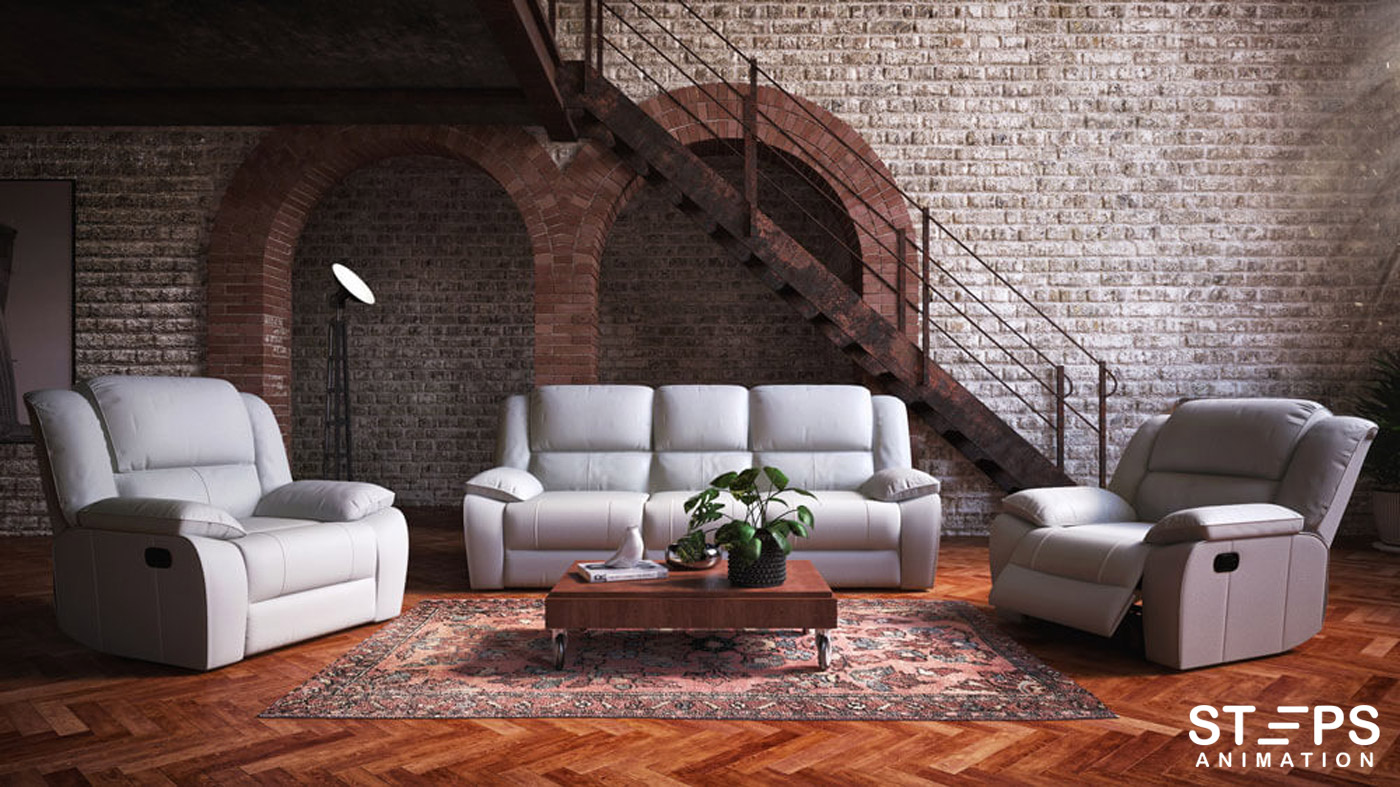
The Benefits of Using 3D Rendering in Architectural Design
3D rendering has brought a multitude of benefits to the field of architectural design. One of the most significant advantages is the ability to visualize and communicate ideas more effectively. In the past, architects had to rely on static blueprints and drawings to convey their visions to clients and stakeholders. However, these two-dimensional representations often fell short in capturing the true essence and experience of the design. With 3D rendering, architects can now create lifelike, immersive visualizations that provide a realistic sense of scale, texture, and lighting. This not only helps clients better understand the design but also allows architects to showcase their creativity and innovation.
Another major benefit of 3D rendering is improved accuracy and precision. With traditional design methods, there was always room for interpretation and miscommunication. However, 3D rendering eliminates these uncertainties by providing a clear and detailed representation of the design. Architects can now spot potential flaws or design issues early on, leading to more efficient problem-solving and ultimately saving time and money. Additionally, 3D rendering allows for easy modifications and iterations, as changes can be made digitally without the need to start from scratch. This level of flexibility and adaptability ensures that the final design meets the client's expectations and requirements.
Furthermore, 3D rendering has revolutionized the design review process. In the past, clients had to rely on their imagination to visualize the final outcome of a project based on static drawings. This often led to misunderstandings and dissatisfaction. However, with 3D rendering, clients can now take virtual tours of their future spaces, exploring every detail and experiencing the design in a way that was previously impossible. This not only enhances the client experience but also fosters a stronger sense of trust and collaboration between architects and their clients.
The Evolution of Architectural Design and the Role of 3D Rendering
Architectural design has come a long way from its humble beginnings. In the early days, architects relied solely on hand-drawn sketches and physical models to communicate their ideas. While these methods served their purpose, they were limited in their ability to provide an accurate representation of the final design. As technology advanced, architects began to experiment with computer-aided design (CAD) software, which allowed for more precise and detailed drawings. However, even with CAD, the designs were still confined to two-dimensional representations.
It wasn't until the introduction of 3D rendering that architectural design truly entered a new era. 3D rendering technology utilizes powerful computer algorithms to create three-dimensional models of architectural designs, complete with realistic lighting, textures, and materials. This breakthrough technology has not only revolutionized the way architects present their ideas but has also opened up a world of possibilities in terms of design exploration and experimentation.
Today, 3D rendering has become an integral part of the design process, enabling architects to create photorealistic visualizations that closely resemble the final product. This level of realism allows architects to better understand the spatial relationships within a design and make informed decisions about materials, lighting, and other essential elements. Additionally, 3D rendering has made it easier for architects to communicate their ideas to clients, stakeholders, and even the general public. By providing a visual representation of the design, architects can effectively convey their vision and generate excitement and support for their projects.
How 3D Rendering Enhances the Client Experience
One of the most significant ways that 3D rendering has revolutionized architectural design is by enhancing the client experience. In the past, clients had to rely on their imagination and interpret two-dimensional drawings to understand how a project would look and feel. This often led to misunderstandings and dissatisfaction, as the final result didn't always match the client's expectations.
With 3D rendering, clients can now take a virtual tour of their future space and experience the design in a way that was previously impossible. By immersing themselves in a lifelike, three-dimensional representation, clients can better understand the scale, proportions, and overall aesthetic of the design. They can walk through the virtual space, exploring every detail and getting a true sense of what it would be like to inhabit the finished project. This level of interactivity and realism not only helps clients make more informed decisions but also fosters a stronger sense of trust and collaboration between architects and their clients.
Furthermore, 3D rendering allows for quick and easy iterations and modifications. Clients can provide feedback on the virtual model, and architects can make changes in real-time, instantly showcasing the updated design. This level of flexibility ensures that the final design meets the client's expectations and requirements, ultimately leading to higher client satisfaction.
The Process of Creating a 3D Rendering in Architectural Design
Creating a 3D rendering requires a multi-step process that involves a combination of technical expertise and artistic creativity. The first step is to gather all the necessary information and data about the project, including architectural drawings, site plans, and design specifications. This information serves as the foundation for the 3D model.
Next, the 3D model is created using specialized software. This involves building a virtual representation of the project, complete with accurate dimensions, spatial relationships, and architectural details. The model can be created from scratch or based on existing CAD drawings. Once the basic structure is in place, textures, materials, and lighting are added to create a realistic and immersive environment.
After the 3D model is complete, the rendering process begins. This involves applying advanced rendering techniques to create high-quality images or animations of the design. The rendering software calculates the behavior of light, shadows, reflections, and other visual elements to produce a realistic representation of the project. The final result is a visually stunning and highly detailed image or animation that brings the design to life.
Tools and Software Used in 3D Rendering for Architectural Design
3D rendering in architectural design relies on a variety of tools and software to bring the virtual models to life. One of the most commonly used software is Autodesk's 3ds Max, which provides a comprehensive set of tools for modeling, rendering, and animation. 3ds Max allows architects to create detailed and realistic 3D models, apply textures and materials, and produce high-quality renderings and animations.
Another popular software is SketchUp, which is known for its user-friendly interface and intuitive design tools. SketchUp is widely used by architects and designers for quick conceptualization and visualization. It allows users to create 3D models, apply textures and materials, and generate realistic renderings with ease.
In addition to these software, architectural rendering often involves the use of other tools and plugins to enhance the workflow and achieve desired effects. These include plugins for realistic lighting simulation, texture mapping, and post-processing effects. With the continuous advancement of technology, new tools and software are constantly being developed, further pushing the boundaries of what is possible in architectural rendering.
Case Studies Showcasing the Impact of 3D Rendering in Architectural Design
To truly understand the transformative power of 3D rendering in architectural design, let's explore a few real-world case studies that highlight its impact.
Case Study 1: The Burj Khalifa
The Burj Khalifa, the tallest building in the world, is a prime example of how 3D rendering played a crucial role in the design and construction process. Using advanced 3D modeling and rendering techniques, the architects were able to visualize the complex structural elements, test different design options, and optimize the building's performance. The realistic visualizations helped the architects communicate their vision to the client and stakeholders, ensuring a smooth and successful project.
Case Study 2: The High Line Park
The High Line Park in New York City is a unique public space built on a historic elevated railway track. 3D rendering played a vital role in the design and development of the park, as it allowed the architects to visualize the proposed design and gain public support. By creating realistic renderings and animations, the architects were able to showcase the park's potential and generate excitement among the community. The visualizations helped stakeholders understand the design intent and contributed to the park's successful transformation from an abandoned railway to a vibrant public space.
Case Study 3: The Sydney Opera House
The Sydney Opera House is an iconic architectural masterpiece that has become a symbol of Australia. 3D rendering played a significant role in the design and construction of this iconic building. By creating detailed 3D models and visualizations, the architects were able to explore different design options and optimize the building's performance. The realistic renderings helped the architects communicate their vision to the client and stakeholders, ensuring that the final design met the client's expectations.
Challenges and Limitations of 3D Rendering in Architectural Design
While 3D rendering has revolutionized architectural design in many ways, it is not without its challenges and limitations. One of the main challenges is the complexity and time-consuming nature of the rendering process. Creating high-quality renderings requires powerful hardware and specialized software, as well as a deep understanding of lighting, materials, and other technical aspects. Additionally, rendering large and complex scenes can be computationally intensive and time-consuming, especially when using advanced rendering techniques.
Another limitation of 3D rendering is the potential for unrealistic expectations. While 3D renderings provide a realistic representation of the design, they are still virtual representations and may not fully capture the experience of being in the actual space. Clients and stakeholders may develop unrealistic expectations based on the renderings, leading to disappointment when the final product is delivered. It is crucial for architects to manage these expectations and clearly communicate the limitations of 3D rendering.
Furthermore, 3D rendering may not be suitable for all types of architectural projects. Certain design elements, such as organic shapes or intricate details, may be challenging to accurately represent in a 3D rendering. In such cases, physical models or other visualization techniques may be more appropriate.
The Future of 3D Rendering in Architectural Design
As technology continues to advance, the future of 3D rendering in architectural design looks promising. With the rise of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), architects and designers will have even more powerful tools at their disposal to create immersive and interactive experiences. VR and AR technologies allow users to step into virtual environments, experiencing the design in a way that was previously unimaginable. This level of interactivity and realism will not only enhance the design process but also revolutionize the way projects are presented and marketed.
Additionally, advancements in real-time rendering will allow for instant feedback and collaboration, further streamlining the design process. Architects will be able to make changes and see the results in real-time, allowing for more efficient decision-making and problem-solving.
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will bring new capabilities to 3D rendering. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data and automatically generate optimized designs based on predefined parameters. This will not only speed up the design process but also open up new possibilities for innovative and sustainable architecture.
In conclusion, 3D rendering has revolutionized the field of architectural design, providing architects and designers with a powerful tool to bring their visions to life. From enhancing communication and collaboration to transforming the client experience, 3D rendering has become an indispensable part of the design process. While it does come with its challenges and limitations, the future of 3D rendering looks incredibly promising, with advancements in VR, AR, real-time rendering, and AI set to reshape the industry. The world of architectural design will never be the same again, thanks to the transformative power of 3D rendering.